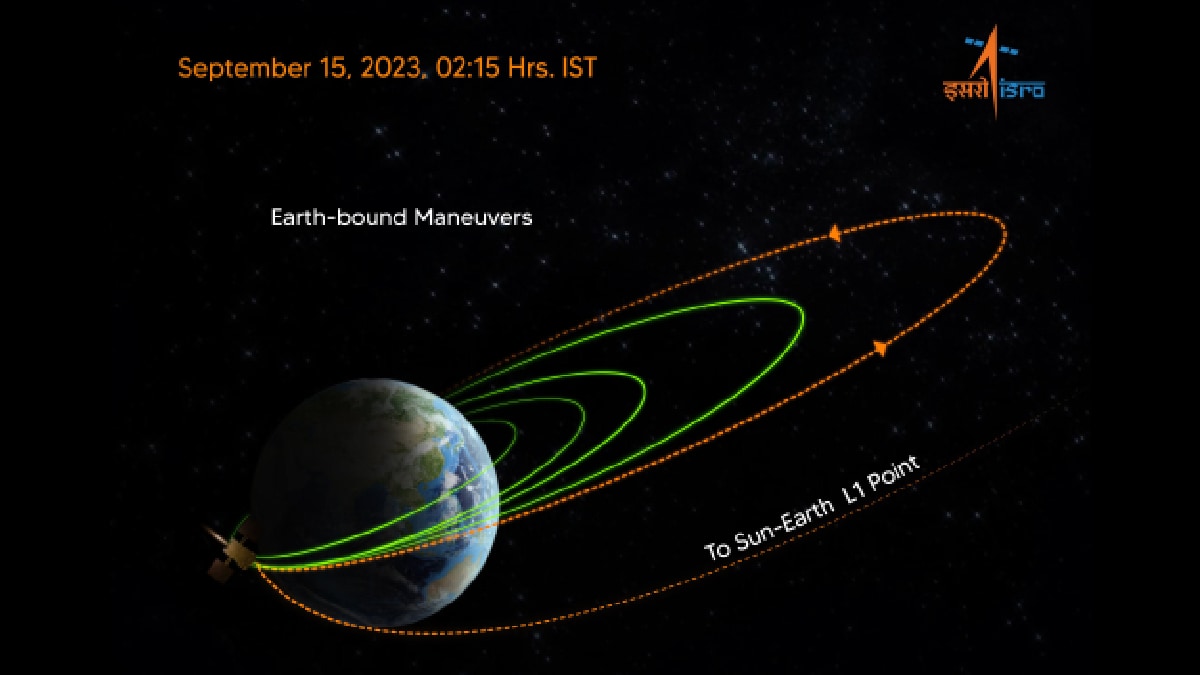
After the change in the orbit, Aditya L-1 has a minimum distance from Earth to 256 km and the maximum distance is 1 lakh 21 thousand 973 kilometers. ISRO has told that the next process of changes in class will be done on September 19 at around 2 pm.
Aditya-l1 mission:
The fourth Earth-Bound Maneuvre (EBN#4) is performed successful.Isro’s Ground Stations at Mauritius, Bengaluru, SDSC-Shar and Port Blair Tracked The Satellite during this operation, while a transportable terminal curren pic.twitter.com/cPFSFSF5gik5
– ISRO (@ISRO) September 14, 2023
Aditya-L-1 is India’s first space based observator. It will study the sun around the first Lagrangeian point (L1) of the Sun-Earth, about 1.5 million kilometers from the Earth. You may find this distance too much, but it is just 1 percent of the total distance of Earth and Sun.
The class of Aditya-L-1 has also been changed earlier. The orbit of the spacecraft was changed three times one after another on three, five and 10 September. Aditya L-1 mission flew on 2 September this month. Its goal is to reach the first Lagrangeian point (L1) of the Sun-Earth. It is a balanced gravitational place between the Earth and the Sun, which is also called ‘Parking’ space agencies.
The L1 point is 1.5 million kilometers from the Earth. Sun can always be monitored from here. When the mission starts its work, ISRO will be able to know solar activities in realtime. Aditya Spacecraft has taken 7 scientific instruments with it. They are all vaikashi and have been prepared by various departments of India. With the help of instruments, different parts of the Sun will be studied.